Fluoride application is a preventive dental treatment that strengthens tooth enamel and increases resistance to cavities. It is especially recommended for children to reduce the risk of tooth decay. Professional fluoride treatments are performed quickly and painlessly by dentists, using high-concentration fluoride gel, varnish, or foam applied to the tooth surfaces.
What Is the Purpose of Fluoride Application?
-
To strengthen enamel and make it more resistant to acid attacks
-
To prevent the formation of new cavities
-
To stop the progression of early-stage tooth decay
-
To reduce tooth sensitivity
Fluoride treatment is particularly effective for protecting primary teeth and newly erupted permanent teeth in children.
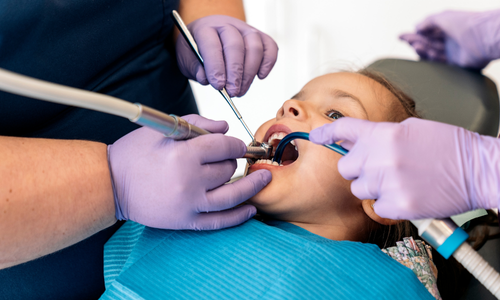
How Is Fluoride Applied?
-
The dentist first cleans and dries the teeth.
-
Fluoride gel, varnish, or foam is applied using a special brush or tray.
-
After application, children should not eat or drink for 30 minutes.
The entire process is completed in 1–2 minutes and is completely painless.
How Often Should Fluoride Be Applied?
For children at high risk of tooth decay, fluoride application may be recommended every 3 to 6 months. The dentist will determine the ideal frequency based on the child’s oral health status and history of cavities.
How Does Fluoride Prevent Cavities?
Fluoride helps maintain essential minerals in tooth enamel. It promotes the remineralization of early-stage cavities and strengthens the enamel against acid attacks. For this reason, fluoride application is a scientifically proven method to reduce the risk of tooth decay.




.png)
.png)
